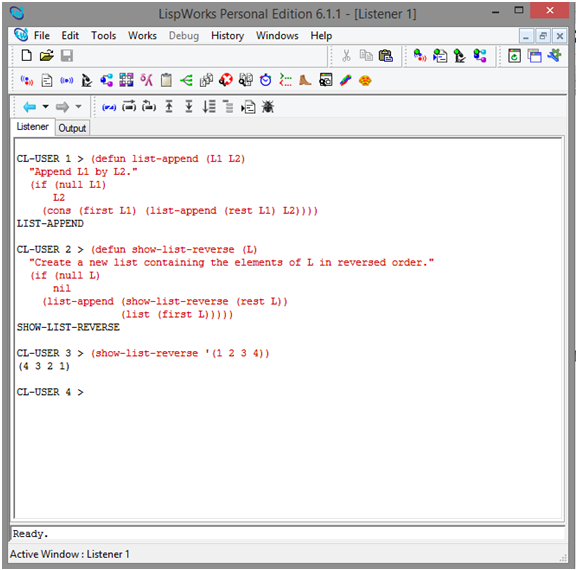
Programs in lisp with output
Define a Recursive LISP function which takes one argument as
a list and return reverse of the list.
SOFTWARE
USED: LispWorks
6.1
THEORY:-
Assuming this is
about Common Lisp, there is a function
one argument as a list and return
reverse of the list. If you use this function which applies a given function to each element of a list and return reverse of the list.
SOURCE
CODE ( IF INCLUDED )
(defun list-append
(L1 L2)
"Append
L1 by L2."
(if (null
L1)
L2
(cons
(first L1) (list-append (rest L1) L2))))
LIST-APPEND
(defun
show-list-reverse (L)
"Create
a new list containing the elements of L in reversed order."
(if
(null L)
nil
(list-append
(show-list-reverse (rest L))
(list
(first L)))))
SHOW-LIST-REVERSE
(show-list-reverse
'(1 2 3 4))
(4
3 2 1)
RESULT:-
CONCLUSION:-
We learned about writing the function to which
takes one argument as a list and return reverse of the list..